The gut ecosystem: at the heart of our immune defence system
The gut is not just an organ dedicated to the transit of food. The gut ecosystem actually consists of 3 components which work together and which each has its own role in the immune defence process, namely:
The gut mucosa
This is the membrane that lines the wall of the digestive tract. It consists of a vast area where exchanges take place between the outside and inside of the body and measures approximately 300 m2, or the size of a tennis court. The mucosa prevents inappropriate microorganisms from entering the body but lets nutrients and micronutrients through. It acts as a “filter”.
The gut immune system
This defends the body against aggressors while allowing food to be tolerated; about 60% of our immune cells are concentrated in the gut.
The gut microbiota
The gut microbiota (and its 100,000 billion bacteria) helps to protect us against pathogens by its barrier effect: the gut bacteria stick to the gut mucosa, preventing pathogenic microorganisms from colonising the gut.
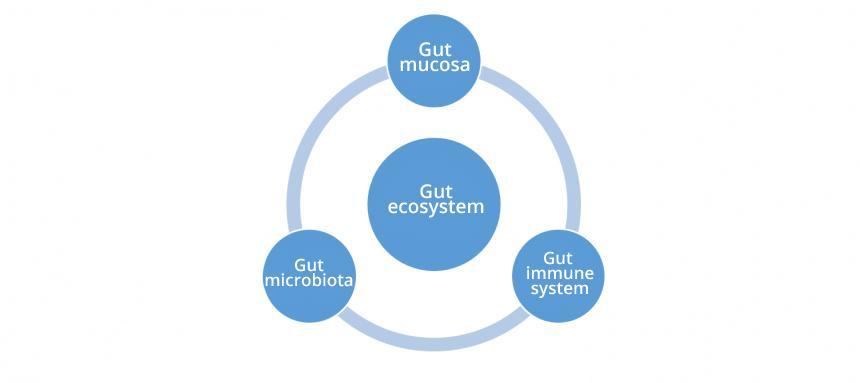
The integrity of this ecosystem is essential for maintaining good immune defences.
Dysbiosis: when the microbiota is out of balance
Some situations, such as poorly managed stress, an unbalanced diet or taking antibiotics for example, can cause an imbalance of the microbiota known as “dysbiosis”. Dysbiosis can upset the balance of the gut ecosystem and consequently weaken our immune defences. However, some friendly bacteria can strengthen the activity of the gut microbiota. These are the probiotics.
Probiotics to support immunity
Les probiotiques sont des micro-organismes vivants qui – administrés en quantité adéquate – modulent positivement la composition et renforcent l’effet barrière du microbiote intestinal. Ils constituent ainsi un complément de bactéries bénéfiques pour la santé1.
Ces bactéries ou levures ont une durée de vie limitée dans le microbiote intestinal (de quelques jours à 2 ou 3 semaines).
Les probiotiques sont présents dans les aliments (yaourts, fromages blancs, fromages) ou disponibles sous forme de compléments alimentaires.
Probiotics are live microorganisms which, when administered in sufficient amounts, can positively modulate the composition and strengthen the barrier effect of the gut microbiota. They are therefore a source of extra bacteria beneficial for health1.
These bacteria or yeasts have a limited lifespan in the gut microbiota (from a few days to 2 or 3 weeks).
Probiotics are contained in foods (yoghurt, fromage blanc or cheese) or available as food supplements.
Lactobacillus probiotics are the most highly recommended for maintaining immunity, more specifically Lactobacillus paracasei and Lactobacillus acidophilus.
Your healthcare professional will be able to advise you and if necessary prescribe supplements to suit your needs.